Human CCL8 / MCP-2 Protein (His Tag)
HC14,MCP-2,MCP2,SCYA10,SCYA8
- 100ug (NPP3935) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10989-H08Y |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Yeast |
| Synonyms | HC14,MCP-2,MCP2,SCYA10,SCYA8 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CCL8 consists of 86 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 10.3 kDa. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 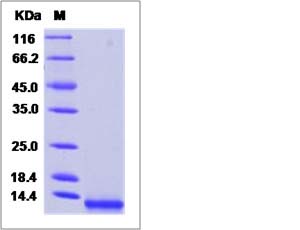 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CCL8 (NP_005614.2) (Gln24-Pro99) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Cytokines & Chemoki and Receptors |Chemokines and Receptors |CC Chemokines and Receptors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Chemokines are a family of small chemotactic cytokines, or proteins secreted by cells. Chemokines share the same structure similarities such as small size, and the presence of four cysteine residues in conserved locations in order to form their 3-dimensional shape. Some of the chemokines are considered pro-inflammatory which can be induced to recruit cells of the immune system to a site of infection during an immune response, while others are considered homeostatic and are implied in controlling the migration of cells during normal processes of tissue maintenance and development. There are four members of the chemokine family: C-C kemokines, C kemokines, CXC kemokines and CX3C kemokines. The C-C kemokines have two cysteines nearby the amino terminus. There have been at least 27 distinct members of this subgroup reported for mammals, called C-C chemokine ligands-1 to 28. Chemokine ligand 8 (CCL8), also known as monocyte chemoattractant protein 2 (MCP-2), is a small cytokine belonging to the C-C chemokine family. CCL8 functions to activate different immune cells, including mast cells, eosinophils and basophils which are involved in allergic responses, monocytes, and T cells and NK cells which are involved in the inflammatory response. CCL8's ability achieves by binding to different cell surface receptors termed chemokine receptors including CCR1, CCR2B and CCR5. It has been reported that CCL8 is a potent inhibitor of HIV-1 by virtue of its binding to CCR5 which is one of the major co-receptors for HIV-1. |
| Reference |
CCL8/MCP-2 related areas, pathways, and other information |
