Human CCNA1 / Cyclin-A1 Protein (His Tag)
CT146
- 100ug (NPP2062) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11013-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CT146 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CCNA1 consists of 483 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 54.6 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 50 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 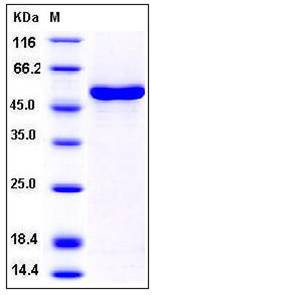 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human CCNA1 isoform a (NP_003905.1) (Met 1-Gln 465) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human His-CCNA1 (P11013-H07B) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CDK1 (P10739-H09B). The EC50 of biotinylated human CDK1 (P10739-H09B) is 0.02-0.04 μg/ml. 2. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human His-CCNA1 (P11013-H07B) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CDK2-His (P10624-H08B). The EC50 of biotinylated human CDK2-His (P10624-H08B)is 0.07-0.15 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cell cycle |Cyclin |Cyclin A Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cyclin A1 is a member of the highly conserved cyclin family that is characterized by a dramatic periodicity in protein abundance, and belongs to the A-type cyclin subfamily. The mammalian A-type cyclin family consists of two members: cyclin A1 and cyclin A2. Different cyclins exhibit distinct expression. Cyclin A1 is expressed in mice exclusively in the germ cell lineage and high rate of cyclinA1 is found in human testis and certain myeloid leukaemia cells. Cyclin A1 is primarily function in the control of meiosis. It serves as regulator subunits binding to cyclin-dependent kinase 1 (Cdk1) and cyclin-dependent kinase 2 (Cdk2), which give two different kinase activities, one appearing in S phase, the other in G2. Through this, cyclin A1 operate the entry and progression in cell cycle. High frequency of cyclin A1 overexpression has been observed in acute myelocytic leukemias, especially those that are at the promyelocyte and myeloblast stages of development. |
| Reference |
