Human CCNE1 / Cyclin-E1 Protein (His Tag)
CCNE
- 100ug (NPP1221) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10902-H07B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CCNE |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CCNE1 consists of 429 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 49.3 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 47 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 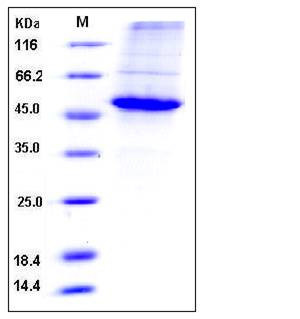 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human CCNE1 isoform 1 (NP_001229.1) (Met 1-Ala 410) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized human CCNE1 (P10902-H07B) at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CDK4 (P10732-H09B), The EC50 of biotinylated human CDK4 (P10732-H09B) is 0.10-0.32 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Cell cycle |other in cell cycle |Cyclin |Cyclin E Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.5, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cyclin E1 is a member of the highly conserved cyclin family and belongs to the E-type cyclin that functions as a regulator of S phase entry and progression in mammalian cells. Cyclin E1 serves as regulatory subunits that bind, activate, and provide substrate for its associated cyclin-dependent kinase2 (CDK2), whose activity is essential for cell cycle G1 / S transition. Over expression of this encoding gene has been found in many tumors, which results in chromosome instability and by extension, induce tumorigenesis. This protein was also found to associate with, and be involved in, the phosphorylation of NPAT protein (nuclear protein mapped to the ATM locus), which participates in cell-cycle regulated histone gene expression and plays a critical role in promoting cell-cycle progression in the absence of pRB. In general, cyclin E1, as an activator of phospho-CDK2 (pCDK2), is important for cell cycle progression and is frequently overexpressed in cancer cells. |
| Reference |
