Human CD10 / Neprilysin / MME Protein
CALLA,CD10,NEP,SFE
- 100ug (NPP3652) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10805-HNCH |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CALLA,CD10,NEP,SFE |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human MME consists of 699 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 80 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhMME migrates as approximately 90-100 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Tyr 52 |
| SDS-PAGE | 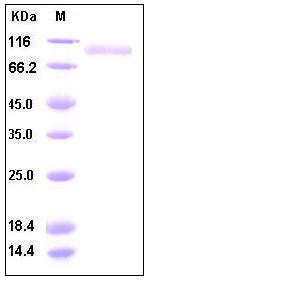 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Tyr 52-Trp 750) of human MME (NP_000893.2) was expressed and purified. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Mca-RPPGFSAFK(Dnp)-OH, (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES005) . The specific activity is >1,000 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Cell Type Marker in Neurodevelopment |Neural Stem Cell (NSC) Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. Cluster of differentiation 10 (CD10), also known as Neprilysin and neutral endopeptidase, is a member of the CD system. CD10 is a zinc-dependent metalloprotease enzyme that had function to degrade a number of small secreted peptides such as the amyloid beta peptide. It exist as a membrane-bound protein and have high concentration in kidney and lung tissues. Mutations in the CD10 gene can induce the familial forms of Alzheimer's disease, providing strong evidence for the protein's association with the Alzheimer's disease process. CD10 is also associated with other biochemical processes. |
| Reference |
