Human CD136 / MST1R Protein (His Tag)
CD136, CDw136, PTK8, RON, MST1R
- 100ug (NPP3661) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11608-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD136, CDw136, PTK8, RON, MST1R |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CD136 consists of 558 amino acids, including the α chain (Glu 25-Arg 309) and the polyhistidine-tagged β chain (Gly 310-Leu 517), and predictes a molecular mass of 60 kDa. (30+30 kDa). As a result of glycosylation, in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCD136 is approximately 70 kDa and 37 kDa, corresponding to the single chain and the cleaved two subunits respectively. |
| predicted N | Glu 25 & Gly 310 |
| SDS-PAGE | 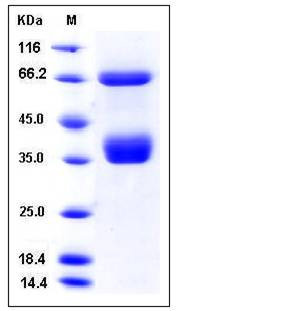 |
| Purity | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the amino acid sequence (Met 1-Leu 571) of human CD136 (Q04912) extracellular domain was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Growth Factor & Receptor |Receptor Tyrosine Kinase (RTK) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The tyrosine kinase receptor, macrophage-stimulating 1 receptor (MST1R), a c-met-related tyrosine kinase, also known as the Ron receptor or CD136, controls cell survival and motility programs related to invasive growth. As tyrosine kinase receptor comprised of an extra-cellular domain, MST1R protein contains the ligand binding pocket and an intracellular region where the kinase domain is located. MST1R signaling may be involved in the regulation of macrophage and T-lymphocyte activation in vivo during injury. This assessment of gene expression indicates the importance of genetic factors in contributing to lung injury, and points to strategies for intervention in the progression of inflammatory diseases. It had been shown that MST1R/CD136 plays a critical role in Ni-induced lung injury in mice. The overexpression of MSP, MT-SP1, and MST1R was a strong independent indicator of both metastasis and death in human breast cancer patients and significantly increased the accuracy of an existing gene expression signature for poor prognosis. Stimulation of MST1R leads to its transphosphorylation and the ultimate activation of numerous intracellular signaling pathways, such as the classical mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway, the phosphotidylinositol (PI)3-kinase pathway, and the JNK pathway. |
| Reference |
