Human CD157 / BST1 Protein (His Tag)
CD157
- 100ug (NPP3672) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10060-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD157 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human BST1 comprises 275 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 31.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rhBST1 migrates as an approximately 38-43 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gly 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 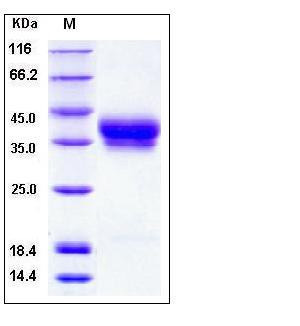 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human BST1 (NP_004325.2) (Met 1-Lys 292) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Cluster of Differentiation (CD) |B Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The cluster of differentiation (CD) system is commonly used as cell markers in immunophynotyping. Different kinds of cells in the immune system can be identified through the surface CD molecules which associating with the immune function of the cell. There are more than 320 CD unique clusters and subclusters have been identified. Some of the CD molecules serve as receptors or ligands important to the cell through initiating a signal cascade which then alter the behavior of the cell. Some CD proteins do not take part in cell signal process but have other functions such as cell adhesion. CD157, also known as ADP-ribosyl cyclase 2, is an ectoenzyme sharing several characteristics with ADP-ribosyl cyclase CD38. CD157 was originally identified as a bone marrow stromal cell molecule (BST-1) with a glycosylphosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchor to bind to the cell surface. CD157 is prevalently expressed by cells of the myeloid lineage. CD157 could act as a receptor with signal transduction capability. Further, it regulates calcium homeostasis and promotes polarization in neutrophils and mediates superoxide (O2−) production in the human U937 myeloid line. |
| Reference |
