Human CD1B / CD1A Protein (Fc Tag)
CD1,CD1A,CD1B,R1
- 100ug (NPP1985) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11831-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD1,CD1A,CD1B,R1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD1B /Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 527 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 58.6 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 59-69 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ser 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 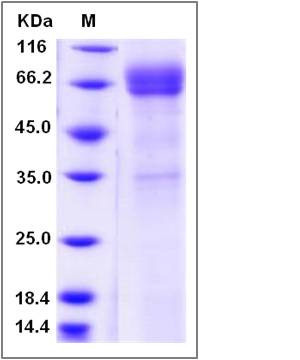 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD1B (NP_001755) (Met1-Ser 303) was expressed, fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |B Cell |B Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD1B contains 1 Ig-like (immunoglobulin-like) domain and belongs to the CD1 family. CD1 family members are transmembrane glycoproteins, which are structurally related to the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) proteins and form heterodimers with beta-2-microglobulin. During protein synthesis and maturation, they bind endogenous lipids that are replaced by lipid or glycolipid antigens when the proteins are internalized and pass through endosomes, before trafficking back to the cell surface. CD1B localizes to late endosomes and lysosomes via a tyrosine-based motif in the cytoplasmic tail, and requires vesicular acidification to bind lipid antigens.. It is expressed on cortical thymocytes, epidermal Langerhans cells, dendritic cells, on certain T-cell leukemias, and in various other tissues. CD1B is an antigen-presenting protein that binds self and non-self lipid and glycolipid antigens and presents them to T-cell receptors on natural killer T-cells. |
| Reference |
