Human CD200 / OX-2 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
MOX1,MOX2,MRC,OX-2,OX2
- 100ug (NPP3679) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10886-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | MOX1,MOX2,MRC,OX-2,OX2 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD200/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 450 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 50.5 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh CD200/Fc monomer is approximately 65-70 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 31 |
| SDS-PAGE | 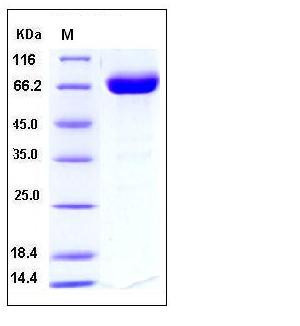 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD200 (NP_005935.4) extracellular domain (Met 1-Gly 232) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized human CD200R1 at 1 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind human CD200 Fc Chimera with a linear range of 0.12-16 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Neuroscience |Neurology process |Neuroinflammation |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD200 (OX-2) is a cell surface glycoprotein that imparts immune privileges by suppressing alloimmune and autoimmune responses through its receptor, CD200R, expressed primarily on myeloid cells. Signals delivered through the CD200:CD200R axis have been shown to play an important role in the regulation of anti-tumor immunity, and overexpression of CD200 has been reported in a number of malignancies, including CLL, as well as on cancer stem cells. The role of CD200-CD200R signaling in immune regulation of the central nervous system has become a popular field of research in recent years. Many studies have shown that there is a close correlation between CD200-CD200R, microglia activation, and Parkinson's disease (PD). The ability of CD200 to suppress myeloid cell activation is critical for maintaining normal tissue homeostasis but may also enhance the survival of migratory neoplastic cells. CD200 and CD200R associate via their respective N-terminal Ig-like domains. CD200 has been characterized as an important immunoregulatory molecule, increased expression of which can lead to decreased transplant rejection, autoimmunity, and allergic disease. Elevated CD200 expression has been reported to be associated with poor prognosis in a number of human malignancies. In addition, CD200 also plays an important role in prevention of graft rejection, autoimmune diseases and spontaneous abortion. |
| Reference |
