Human CD28 Protein (Fc Tag)
Tp44
- 100ug (NPP1136) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11524-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Tp44 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD28/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 375 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 42 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCD28/Fc monomer is approximately 55-65 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asn 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 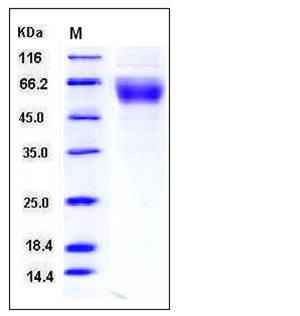 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD28 isoform 1 (P10747-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Pro 152) was was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |T Cell |T Cell CD Antigen |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD28 (Cluster of Differentiation 28) is a disulphide-bonded glycoprotein belonging to the immunoglobulin (Ig) superfamily, and structurally consists of a single Ig V-like extracellular domain, a transmembrane domain and an intracellular domain. Mouse CD28 is constitutively expressed on the surface of all murine T cells and on developing thymocytes as disulfide-linked homodimers or as monomers. CD28 can binds the B7-1 and B7-2 ligand, and together perform important functions in the T and B cell response pathways. B7/CD28 family members, which can augment or antagonize T-cell receptor signaling, in the regulation of central and peripheral T-cell tolerance. CD28 is thus involved in T-cell activation, the induction of cell proliferation and cytokine production and promotion of T-cell survival. |
| Reference |
