Human CD33 / Siglec-3 Protein (Fc Tag)
p67,Siglec-3,SIGLEC3
- 100ug (NPP3688) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12238-H05H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | p67,Siglec-3,SIGLEC3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD33/mFc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer comprises 476 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 53.1 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of the protein is approximately 64-68 in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Asp 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 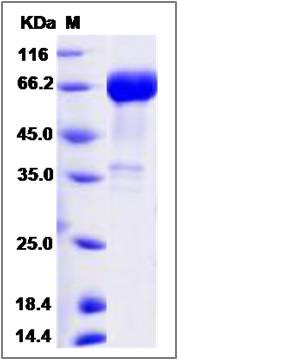 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD33 (AAH28152.1) (Met1-His259) was fused with Fc region of mouse IgG at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Myeloid cell surface antigen CD33 also known as Sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin 3, CD33 antigen or Siglec-3, is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and SIGLEC (sialic acid binding Ig-like lectin) family. This Single-pass type I membrane protein contains 1 Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain and 1 Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. CD33 /Siglec-3 is a putative adhesion molecule of myelomonocytic-derived cells that mediates sialic-acid dependent binding to cells. CD33 /Siglec-3 preferentially binds to alpha-2,6-linked sialic acid. The sialic acid recognition site may be masked by cis interactions with sialic acids on the same cell surface. In the immune response, may act as an inhibitory receptor upon ligand induced tyrosine phosphorylation by recruiting cytoplasmic phosphatase(s) via their SH2 domain(s) that block signal transduction through dephosphorylation of signaling molecules. CD33/Siglec-3 induces apoptosis in acute myeloid leukemia (in vitro). CD33/Siglec-3 can function as a sialic acid-dependent cell adhesion molecule and that binding can be modulated by endogenous sialoglycoconjugates when CD33 is expressed in a plasma membrane. |
| Reference |
