Human CD3e / CD3 epsilon Protein (His & Fc Tag)
CD3 epsilon,IMD18,T3E,TCRE
- 100ug (NPP3695) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10977-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD3 epsilon,IMD18,T3E,TCRE |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CD3E is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer comprises 355 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 40 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, it migrates as an approximately 44-53 and 38 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 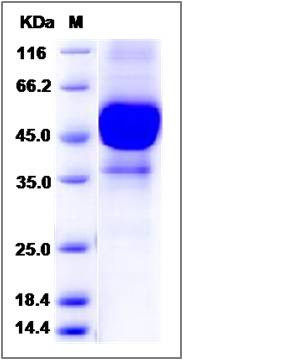 |
| Purity | (84.6+14.1) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD3E (Met 1-Asp126) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Inflammatory Cytokines & Chemoki and Receptors |IL-12 Family |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | T-cell surface glycoprotein CD3 epsilon chain, also known as CD3E, is a single-pass type I membrane protein. CD3E contains 1 Ig-like (immunoglobulin-like) domain and 1 ITAM domain. CD3E, together with CD3-gamma, CD3-delta and CD3-zeta, and the T-cell receptor alpha/beta and gamma/delta heterodimers, forms the T cell receptor-CD3 complex. The CD3 epsilon subunit of the T cell receptor (TCR) complex contains two defined signaling domains, a proline-rich sequence and an immune tyrosine activation motifs (ITAMs), and this complex undergoes a conformational change upon ligand binding that is thought to be important for the activation of T cells. In the CD3 epsilon mutant mice, all stages of T cell development and activation that are TCR-dependent were impaired, but not eliminated, including activation of mature naïve T cells with the MHCII presented superantigen, staphylococcal enterotoxin B, or with a strong TCR cross-linking antibody specific for either TCR-Cbeta or CD3 epsilon. T cell receptor-CD3 complex plays an important role in coupling antigen recognition to several intracellular signal-transduction pathways. This complex is critical for T-cell development and function, and represents one of the most complex transmembrane receptors. CD3E plays an essential role in T-cell development, and defects in CD3E gene cause severe immunodeficiency. Homozygous mutations in CD3D and CD3E genes lead to a complete block in T-cell development and thus to an early-onset severe combined immunodeficiency phenotype. |
| Reference |
