Human CD40 / TNFRSF5 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
Bp50,CDW40,p50,TNFRSF5
- 100ug (NPP1031) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10774-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Bp50,CDW40,p50,TNFRSF5 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CD40/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 421 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 47.3 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhCD40/Fc monomer migrates with an apparent molecular mass of 55-60 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Glu 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 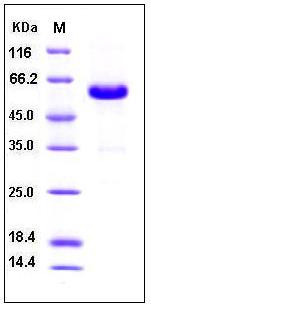 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CD40 (NP_001241.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Arg193) was fused with the C-terminal polyhistidine-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized recombinant human CD40 at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CD40L with a linear range of 7.8-125 ng/ml . |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Cytokine |TNF Superfamily |Processes Regulated by TNF Superfamily Members |Regulation of T Cell Co-stimulation by TNF Superfamily Members | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM Glycine, 10mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD40, also known as TNFRSF5, is a member of the TNF receptor superfamily which are single transmembrane-spanning glycoproteins. CD40 protein plays an essential role in mediating a broad variety of immune and inflammatory responses including T cell-dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory B cell development, and germinal center formation. CD40 protein is expressed in B cells, dendritic cells, macrophages, endothelial cells, and several tumor cell lines. Defects in CD40 result in hyper-IgM immunodeficiency type 3 (HIGM3). In addition, CD40/CD40L interaction is found to be necessary for amyloid-beta-induced microglial activation, and thus is thought to be an early event in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. |
| Reference |
