Human CD73 / NT5E Protein (His Tag)
CALJA,CD73,E5NT,eN,eNT,NT,NT5,NTE
- 100ug (NPP3713) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10904-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CALJA,CD73,E5NT,eN,eNT,NT,NT5,NTE |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human NT5E consists of 532 amino acids with the predicted molecular mass of 59.2 kDa. |
| predicted N | Trp 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 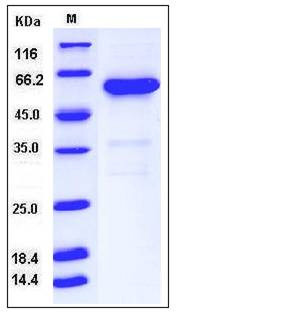 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human NT5E (NP_002517.1) (Met 1-Lys 547) without the propeptide was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to hydrolyze the 5’phosphate group from the substrate adenosine 5’monophosphate (AMP). The specific activity is > 20,000 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolism processes |Hypoxia | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, 120 mM NaCl, 4 mM CaCl2, 20 % glycerol, pH 7.5. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | 5'-nucleotidase, also known as NT5E, NTE, and CD73, is a cell membrane protein which belongs to the 5'-nucleotidase family. CD73 is a glycosyl phosphatidylinositol (GPI) anchored purine salvage enzyme expressed on the surface of human T and B lymphocytes. CD73 catalyzes the conversion of purine and pyrimidine ribo- and deoxyribonucleoside monophosphates to the corresponding nucleosides. CD73 serves as a costimulatory molecule in activating T cells. CD73 generated adenosine functions in cell signalling in many physiologic systems, including intestinal epithelium, ischemic myocardium, and cholinergic synapses. CD73 might mediate lymphocyte-stromal cell interactions or condition the local microenvironment to facilitate lymphocyte development and/or function. In CD73-depleted cells, surface levels of the leukocyte adhesion molecules ICAM-1, VCAM-1 and E-selectin increase. CD73 produces extracellular adenosine, which then acts on G protein-coupled purigenic receptors to induce cellular responses. CD73 has also been reported to regulate expression of pro-inflammatory molecules in mouse endothelium. |
| Reference |
