Human CD86 / B7-2 Protein (His & Fc Tag)
B7-2,B7.2,B70,CD28LG2,LAB72
- 100ug (NPP1188) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10699-H03H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | B7-2,B7.2,B70,CD28LG2,LAB72 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human B7-2/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 467 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 53.2 kDa. In SDS-PAGE, the apparent molecular mass of rh B7-2/Fc monomer is approximately 80-90 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Leu 20 |
| SDS-PAGE | 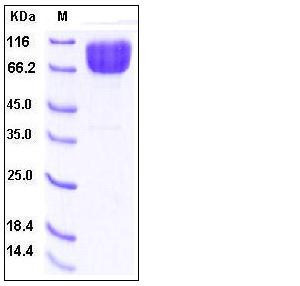 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain (Met 1-His 239) of human B7-2 (NP_008820.2) pro-protein was fused with the C-terminal His-tagged Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind human CD28 in a functional ELISA. 2. Measured by its ability to induce IL2 secretion by Jurkat human acute T cell leukemia cells. The ED50 for this effect is 1-5μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Adaptive Immunity |Regulatory T Cells |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CD86, also known as B-lymphocyte activation antigen B7-2 (referred to as B70), is a member of the cell surface immunoglobulin superfamily. B7-2 exists predominantly as a monomer on cell surfaces and interacts with two co-stimulatory receptors CD28 and cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 (CTLA-4) expressed on T cells, and thus induces the signal pathways which regulate T cell activation and tolerance, cytokine production, and the generation of CTL. It is indicated that contacts between B and T helper cells mediated by CD86 encourage signals for the proliferation and IgG secretion of normal B cells and B cell lymphomas. Recent study has revealed that CD86 also promotes the generation of a mature APC repertoire and promotes APC function and survival. CD86 has an important role in chronic hemodialysis, allergic pulmonary inflammation, arthritis, and antiviral responses, and thus is regarded as a promising candidate for immune therapy. |
| Reference |
