Human CDC37 / CDC37A Protein (GST Tag)
P50CDC37
- 100ug (NPP1193) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10647-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | P50CDC37 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDC37/GST chimera consists of 603 amino acids and has a predicted a molecular mass of 70.7 kDa as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 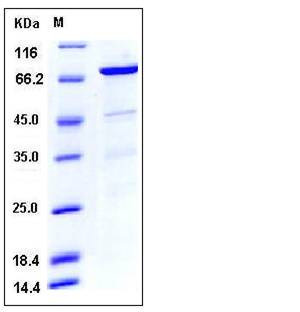 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human CDC37 (NP_008996.1) (Met 1-Val 378) was fused with the GST tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Transcription Factors and Regulators |Basic Helix-Loop-Helix (bHLH) Transcription Factors |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 0.5mM GSH, 0.5mM PMSF, 10% glycerol, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CDC37 is a protein that is expressed in proliferative zones during embryonic development and in adult tissues, consistent with a positive role in proliferation and is required for cell division in budding yeast. CDC37 is though to play an important role in the establishment of signaling pathways controlling cell proliferation through targeting intrinsically unstable oncoprotein kinases such as Cdk-4, Raf-1, and src to the molecular chaperone Hsp90. Decreased Hsp90 expression can reduce the levels of microtubule-associated protein tau, whose overexpression may induce many diseases. CDC37 is considered as a co-chaperone that is classified to Hsp90's accessory proteins. It has been reported that suppression of Cdc37 destabilized tau, leading to its clearance, whereas cdc37 overexpression preserved tau.Cdc37 was found to co-localize with tau in neuronal cells and to physically interact with tau from human brain. Moreover, Cdc37 levels significantly increased with age. |
| Reference |
