Human CDK2 / p33 Protein (His Tag)
CDKN2,p33(CDK2)
- 100ug (NPP3730) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10624-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CDKN2,p33(CDK2) |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDK2 consists of 308 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 35 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhCDK2 is approximately 33 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 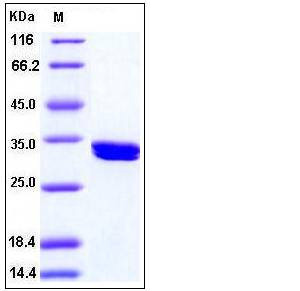 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human cyclin-dependent kinase 2 isoform 1 (NP_001789.2) (Met 1-Leu 298) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Akt Pathway |Intracellular Kinases in the Akt Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CDK2 is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. This protein kinase is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28, and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the cyclin-dependent protein kinase complex, whose activity is restricted to the G1-S phase, and essential for cell cycle G1/S phase transition. Cdks (cyclin-dependent kinases) are heteromeric serine/threonine kinases that control progression through the cell cycle in concert with their regulatory subunits, the cyclins. Cdks are constitutively expressed and are regulated by several kinases and phosphastases, including Wee1, CDK-activating kinase and Cdc25 phosphatase. Although there are 12 different cdk genes, only 5 have been shown to directly drive the cell cycle (Cdk1, -2, -3, -4, and -6). Following extracellular mitogenic stimuli, cyclin D gene expression is upregulated. Cdk4 forms a complex with cyclin D and phosphorylates Rb protein, leading to liberation of the transcription factor E2F. E2F induces transcription of genes including cyclins A and E, DNA polymerase and thymidine kinase. Cdk4-cyclin E complexes form and initiate G1/S transition. Subsequently, Cdk1-cyclin B complexes form and induce G2/M phase transition. Cdk1-cyclin B activation induces the breakdown of the nuclear envelope and the initiation of mitosis. CDK2 associates with and regulated by the regulatory subunits of the complex including cyclin A or E, CDK inhibitor p21Cip1 (CDKN1A) and p27Kip1 (CDKN1B). Its activity is also regulated by its protein phosphorylation. CDK2 is involved in the control of the cell cycle. It also interacts with cyclins A, B1, B3, D, or E. Activity of CDK2 is maximal during S phase and G2. |
| Reference |
