Human CDK4 / CMM3 Protein (GST Tag)
CMM3,PSK-J3
- 100ug (NPP3731) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10732-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CMM3,PSK-J3 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDK4/GST chimera consists of 528 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 60 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 55 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 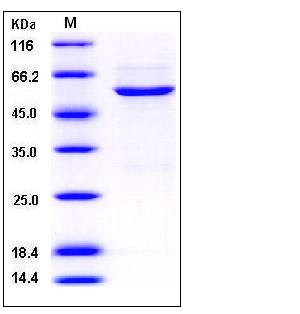 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CDK4 (NP_000066.1) (Met 1-Glu 303) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | No Kinase Activity |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Cyclin-Dependent Kinase (CDK) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, 10% gly, 0.5mM PMSF, pH 8.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CDK4 is a member of the Ser/Thr protein kinase family. It is highly similar to the gene products of S. cerevisiae cdc28 and S. pombe cdc2. It is a catalytic subunit of the protein kinase complex that is important for cell cycle G1 phase progression. The activity of CDK4 is restricted to the G1-S phase, which is controlled by the regulatory subunits D-type cyclins and CDK inhibitor p16(INK4a). CDK4 was shown to be responsible for the phosphorylation of retinoblastoma gene product. CDK4 is the ser/Thr-kinase component of cyclin D-CDK4 (DC) complexes that phosphorylate and inhibit members of the retinoblastoma (RB) protein family including RB1 and regulate the cell-cycle during G(1)/S transition. Phosphorylation of RB1 allows dissociation of the transcription factor E2F from the RB/E2F complexes and the subsequent transcription of E2F target genes which are responsible for the progression through the G(1) phase. Hypophosphorylates RB1 in early G(1) phase. Cyclin D-CDK4 complexes are major integrators of various mitogenenic and antimitogenic signals. CDK4 has been shown to be mutated in some types of cancer, whilst a chromosomal rearrangement can lead to Cdk6 overexpression in lymphoma, leukemia and melanoma. |
| Reference |
