Human CDKN2D / p19ink4d Protein (GST Tag)
INK4D,p19,p19-INK4D
- 100ug (NPP3733) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12558-H09E |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | E. coli |
| Synonyms | INK4D,p19,p19-INK4D |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDKN2D/GST chimera consists of 400 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 44.9 kDa. It migrates as an approxiamtely 46 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 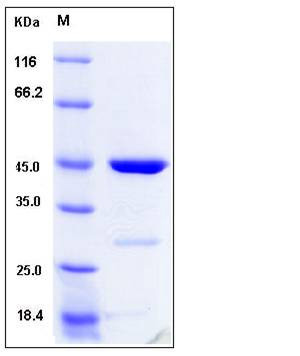 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CDKN2D (P55273) (Met 10Leu 166) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Immobilized human GST-CDKN2D at 10 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human GST-CDK4 (P10732-H09B), The EC50 of biotinylated human GST-CDK4 (P10732-H09B) is 0.52-1.2 μg/ml. |
| Research Area | Epigenetics |Cell cycle |Cell Cycle Inhibitor |Inhibitors of CDK4 (Ink4) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 2D(also known as CDKN2D or p19ink4d), a member of the INK4 family of cyclin-dependent kinase (CDK) inhibitors, negatively regulates the cyclin D-CDK4/6 complexes, which promote G1/S transition by phosphorylating the retinoblastoma tumor-suppressor gene product. It is clearly shown that DNA repair is the main target of p19ink4d effect and that diminished apoptosis is a downstream event. Experiments has uncovered a role of p19INK4d as a regulator of DNA-damage-induced apoptosis and suggest that it protects cells from undergoing apoptosis by allowing a more efficient DNA repair. It has been demonstrated that p19INK4d expression enhances cell survival under genotoxic conditions. Previous work has shown that inactivation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) p19(Ink4d) leads to progressive hearing loss attributable to inappropriate DNA replication and subsequent apoptosis of hair cells. It may also involved in male reproductive function including testicular atrophy, alteration in serum follicle stimulating hormone, qualitative increase in germ cell apoptosis, and delayed kinetics of meiotic prophase markers. |
| Reference |
