Human CDON / CDO Protein (His Tag)
CDO,CDON1,HPE11,ORCAM
- 100ug (NPP3734) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11965-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CDO,CDON1,HPE11,ORCAM |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDON consists of 949 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 103 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 125 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Asp 26 |
| SDS-PAGE | 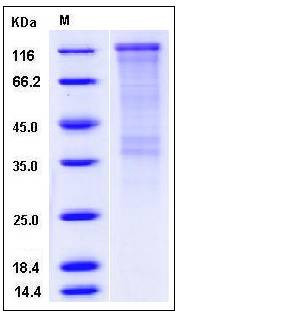 |
| Purity | > 65 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CDON (AAI14436.1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Asp 963) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Representative pathway |Hedgehog Signaling Pathway |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cell adhesion molecule-related, down-regulated by oncogenes (CDON), also known as CDO, is an Ig superfamily member, is a component of a cell surface receptor that positively regulates skeletal myogenesis. Brother of CDO (BOC) is a cell surface receptor that derives its name from the structurally related protein, CDON. They are components of a cell surface receptor that positively regulates myogenesis in vitro. Expression of Cdo and Boc in myoblast cell lines is downregulated by the ras oncogene, and forced re-expression of either Cdo or Boc can override ras-induced inhibition of myogenic differentiation. CDO and BOC play a role in the inverse relationship between differentiation and transformation of cells in the skeletal muscle lineage. CDON binds to Bnip-2 and JLP, scaffold proteins for Cdc42 and p38alpha/beta MAPK, respectively. The Bnip-2/Cdc42 and JLP/p38alpha/beta complexes associate in a CDON-dependent manner, resulting in Bnip-2/Cdc42-dependent p38alpha/beta activation and stimulation of cell differentiation. It is proposed that CDO mediates, at least in part, the effects of cell-cell interactions between muscle precursors that are critical in myogenesis. |
| Reference |
