Human CEACAM1 / CD66a Protein (His Tag)
BGP,BGP1,BGPI,CD66a,CEACAM‑1
- 100ug (NPP3735) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10822-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | BGP,BGP1,BGPI,CD66a,CEACAM‑1 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CEACAM1 comprises 405amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 45 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhCEACAM1 is approximately 65-85 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 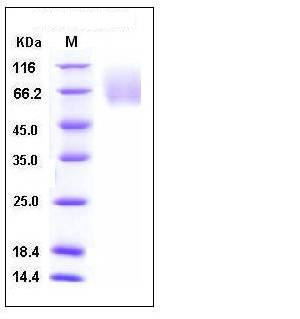 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human CEACAM1 (NP_001020083.1) (Met 1-Gly 428) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated Human CEACAM6-His (P10823-H08H) in functional ELISA. 2. Measured by its ability to bind biotinylated Human CEACAM8-His (P11729-H08H) in functional ELISA. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |ITIM/ITAM Immunoreceptors and Related Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The carcinoembryonic-antigen-related cell-adhesion molecule (CEACAM) family of proteins has been implicated in various intercellular-adhesion and intracellular-signalling-mediated effects that govern the growth and differentiation of normal and cancerous cells. CEACAM1, also known as biliary glycoprotein I (BGP I) and CD66a, is a member of the carcinoembryonic antigen (CEA) gene family which belongs to the immunoglobulin superfamily. The highly glycosylated CEACAM1 contains one N-terminal V-type Ig-like domain and three C2-type Ig-like domains within its ECD, and one ITIM motif and a calmodulin binding site in the cytoplasmic region. CEACAM1 is a surface glycoprotein expressed on various blood cells, epithelial cells, and vascular cells. It was described as an adhesion molecule mediating cell adhesion via both homophilic and heterophilic manners, and was detected on leukocytes, epithelia, and endothelia. Studies have revealed that CEACAM1 performs actions in multiple cellular processes including tissue differentiation, angiogenesis, apoptosis, metastasis, as well as the modulation of innate and adaptive immune responses. |
| Reference |
