Human CEACAM5 / CD66e Protein (His Tag)
CD66e,CEA
- 100ug (NPP3736) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11077-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD66e,CEA |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CEACAM5 consists of 662 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 72.8 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCEACAM5 is approximately 100-110 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Lys 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 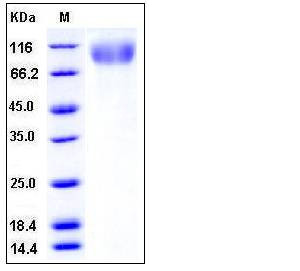 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human CEACAM5 (NP_004354.2) (Met 1-Ala 685) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Tumor biomarker |Tumor Suppressor |Other in Tumor suppressor |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CEACAM5, also known as CEA or D66e, belongs to the large CEACAM subfamily of immunoglobulin superfamily. CEACAM5 is expressed primarily by epithelial cells, and is synthesized as a glycoprotein with a MW of 180 kDa comprising 60% carbohydrate. CEACAM5 contains one Ig-like V-type domain at the N-terminus, followed by six Ig-like C2-type domain and a GPI anchor, and exists as a homodimer. CEACAM5 and CEACAM6 are overexpressed in many cancers and are associated with adhesion and invasion. CEACAM5 can mediate cell-cell adhesion through homotypic and heterotypic interactions. It functions as a homotypic intercellular adhesion molecule and serves as a widely used tumor marker, since it is expressed at higher levels in tumorous tissues than in corresponding normal tissues. CEACAM5 has also been shown to contribute to tumorigenicity by inhibiting cellular differentiation. In addition, CEACAM5 is identified as the host receptor for the Dr family of adhesins of E.Coli, and the binding of E.coli Dr adhesins leads to dissociation of the CEACAM5 homodimer. |
| Reference |
