Human CEACAM6 / CD66c Protein (His Tag)
CD66c,CEAL,NCA
- 100ug (NPP2000) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10823-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD66c,CEAL,NCA |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CEACAM6 comprises 297 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 32.6 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, rh CEACAM6 migrates as an approximately 45-55 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Lys 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 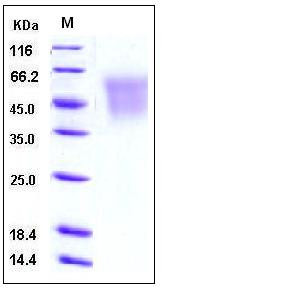 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CEACAM6 (NP_002474.3) (Met 1-Gly 320) with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human CEACAM6-his (P10823-H08H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CEACAM8-his, The EC50 of biotinylated human CEACAM8-his is 0.17 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Embryogenesis |Germ Layer Formation |Ectoderm Marker |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carcinoembryonic antigen-related cell adhesion molecule 6 (CEACAM6), also known as nonspecific crossreacting antigen (NCA) and CD66c, is one of seven human CEACAM family members within the immunoglobulin superfamily. It s a glycosylphosphatidylinositol-linked immunoglobulin superfamily member that is overexpressed in a variety of human cancers, including colon, breast and lung and is associated with tumourigenesis, tumour cell adhesion, invasion and metastasis. CEACAM6 is a unique mediator of migration and invasion of drug resistant oestrogen-deprived breast cancer cells, and this protein could be an important biomarker of metastasis. CEACAM6 is expressed by granulocytes and their progenitors. It is also expressed by epithelia of various organs and is upregulated in pancreatic and colon adenocarcinomas, as well as hyperplastic polyps. Resistance to adhesion-related apoptosis in tumor cells is conferred in the condition of CEACAM6 overexpression. |
| Reference |
