Human CEACAM8 / CD66b Protein (His Tag)
CD66b,CD67,CGM6,NCA-95
- 100ug (NPP3738) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11729-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD66b,CD67,CGM6,NCA-95 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CEACAM8 consists of 296 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 32.8 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh CEACAM8 is approximately 55-60 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 35 |
| SDS-PAGE | 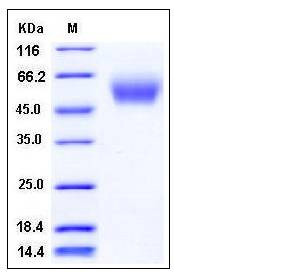 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CEACAM8 (NP_001807.2) without the pro peptide (Met 1-Ser319) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human CEACAM6-his (P10823-H08H) at 10 μg/mL (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CEACAM8-his, The EC50 of biotinylated human CEACAM8-his is 0.17 μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Myeloid Cells |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CEACAM8, also known as CD66b or NCA-95, is a single chain, GPI-anchored, highly glycosylated protein belonging to the carcinoembryonic antigen family. There are four members in this family: CD66a, CD66b, CD66c, and CD66d. Members of CEACAM family are widely expressed especially on human neutrophils, and, depending on the tissue, capable of regulating diverse functions including tumor promotion, tumor suppression, angiogenesis, and neutrophil activation. Abnormal overexpression and downregulation of some CEACAMs have been described in tumor cells. Monoclonal antibodies grouped in the CD66 cluster recognize CEACAM members. Ectopic CD66 expression is commonly detected in B-cell lineage acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). CEACAM8(CD66b) is also an activation marker for human granulocytes. However, its biological functions are largely unknown in eosinophils. It has been reported that CD66b is highly expressed on the surface of human peripheral blood eosinophils isolated from healthy individuals. Engagement of CD66b by mAb or a natural ligand, galectin-3, activated a Src kinase family molecule, hemopoietic cell kinase (Hck), and induced cellular adhesion, superoxide production, and degranulation of eosinophils. CD66b molecules were localized in lipid rafts, and disruption of lipid rafts or removal of the GPI anchor inhibited the adhesion and activation of eosinophils. Importantly, CD66b was constitutively and physically associated with a beta2 integrin, CD11b, and cross-linking of CD66b induced a striking clustering of CD11b molecules. Thus, CD66b molecules are involved in regulating adhesion and activation of eosinophils, possibly through their localization in lipid rafts and interaction with other cell surface molecules, such as CD11b. Binding of exogenous or endogenous carbohydrate ligands(s) to CD66b may be important in the release of proinflammatory mediators by human eosinophils. |
| Reference |
