Human CES2 / Carboxylesterase-2 Protein (His Tag)
CE-2,CES2A1,iCE,PCE-2
- 100ug (NPP2003) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10380-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CE-2,CES2A1,iCE,PCE-2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CES2 comprises 544 amino acids with a predicted molecular mass of 60.4 kDa, as estimated in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 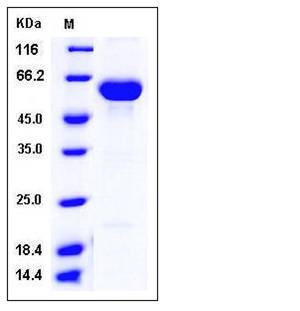 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CES2 isoform 1 (O00748-1) (Met 1-Leu 559) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Lipid metabolism |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM NaAc, 150mM NaCl, 10% Glycerol, pH 5.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carboxylesterase 2 (CES2) is a member of the carboxylesterase family and belongs to the multigene family. Carboxylesterase 2 is responsible for the hydrolysis of ester- and amide-bond-containing drugs such as cocaine and beroin. It also serves to hydrolyze long-chain fatty acid esters and thioesters. It is speculated that carboxylesterases may play a role in lipid metabolism and the blood-brain barrier system and together with isform 1, are a serine esterase involved in both drug metabolism and activation. Human carboxylesterase 2 is commonly expressed in tumor tissues and irinotecan, a topoisomerase I inhibitor commonly used in the treatment of many solid tumors. |
| Reference |
