Human CLEC12A / CLL-1 / DCAL2 Protein (His Tag)
CLL-1,CLL1,DCAL-2,MICL
- 100ug (NPP3742) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11896-H07H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CLL-1,CLL1,DCAL-2,MICL |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CLEC12A consists of 221 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 26 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhCLEC12A is approximately 40-45 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | His |
| SDS-PAGE | 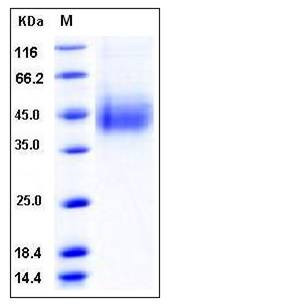 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CLEC12A (EAW96132.1) extracellular domain (His 75-Ala 275) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Lectin |C-tyep lectin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CLEC12A is a member of the C-type lectin/C-type lectin-like domain (CTL/CTLD) superfamily. Members of this family share a common protein fold and have diverse functions, such as cell adhesion, cell-cell signaling, glycoprotein turnover, and roles in inflammation and immune response. CLEC12A is a negative regulator of granulocyte and monocyte function. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene have been described, but the full-length nature of some of these variants has not been determined. C-type lectins are the most diverse and prevalent lectin family in immunity. Using a novel CLEC12A -specific monoclonal antibody, experiments had shown that human CLEC12A was expressed primarily on myeloid cells, including granulocytes, monocytes, macrophages, and dendritic cells. Although CLEC12A was highly N-glycosylated in primary cells, the level of glycosylation was found to vary between cell types. CLEC12A surface expression was down-regulated during inflammatory/activation conditions in vitro, as well as during an in vivo model of acute inflammation. This suggests that CLEC12A may be involved in the control of myeloid cell activation during inflammation. |
| Reference |
