Human CLPS / Colipase Protein (His Tag)
CLPS
- 100ug (NPP3745) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13631-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | CLPS |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CLPS consists of 105 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 11.5 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 12 KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 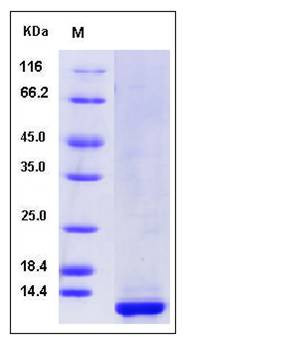 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CLPS (P04118) (Met 1-Gln 112) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | 1. Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. 2. Immobilized human CLPS-His at 10μg/mL(100μL/well) can bind biotinylated human PNLIP-His (P13564-H08H). The EC50 of biotinylated human PNLIP-His (P13564-H08H) is 0.57-1.33μg/mL. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Lipids / Lipoproteins |Lipid Metabolism |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, 500mM NaCl, pH 7.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Colipase belongs to the colipase family. Structural studies of the complex and of colipase alone have revealed the functionality of its architecture. It is a small protein with five conserved disulphide bonds. Structural analogies have been recognised between a developmental protein, the pancreatic lipase C-terminal domain, the N-terminal domains of lipoxygenases and the C-terminal domain of alpha-toxin. Colipase can only be detected in pancreatic acinar cells, suggesting regulation of expression by tissue-specific elements. Colipase allows lipase to anchor noncovalently to the surface of lipid micelles, counteracting the destabilizing influence of intestinal bile salts. Without colipase the enzyme is washed off by bile salts, which have an inhibitory effect on the lipase. Colipase is a cofactor needed by pancreatic lipase for efficient dietary lipid hydrolysis. It binds to the C-terminal, non-catalytic domain of lipase, thereby stabilising as active conformation and considerably increasing the overall hydrophobic binding site. |
| Reference |
