Human COMP Protein (His Tag)
EDM1,EPD1,MED,PSACH,THBS5
- 100ug (NPP2044) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10173-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | EDM1,EPD1,MED,PSACH,THBS5 |
| Molecular Weight | The mature form of human COMP consists of 748 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and predicts a molecular mass of 82.4 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rhCOMP is approximately 120-130 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 21 |
| SDS-PAGE | 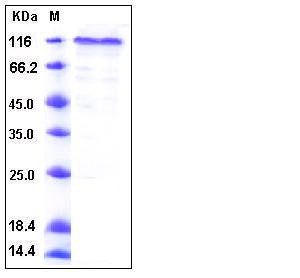 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human COMP (NP_000086.2) precusor (Met 1-Ala 757) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Extracellular Matrix |ECM Proteins |Thrombospondin | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cartilage Oligomeric Matrix Protein (COMP), also referred to as Thrombospondin-5, is a non-collagenous extracellular matrix (ECM) protein and belongs to the subgroup B of the thrombospondin protein family. This protein is expressed primarily in cartilage, ligament, and tendon, and binds to other ECM proteins such as collagen I, II and IX with high affinities depending on the divalent cations Zn2+ or Ni2+. COMP is a secreted glycoprotein that is important for growth plate organization and function. It is suggested to play a role in cell growth and development, and recent studies have revealed the possible mechanism that it protects cells against death by elevating members of the IAP (inhibitor of apoptosis protein) family of survival proteins. Mutations in COMP cause two skeletal dysplasias, pseudoachondroplasia (PSACH) and multiple epiphyseal dysplasia (EDM1), and up-regulated expression of COMP are observed in rheumatoid arthritis and certain carcinomas. |
| Reference |
