Human COQ7 Protein (His Tag)
CAT5,CLK-1,CLK1
- 100ug (NPP3766) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P12195-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CAT5,CLK-1,CLK1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human COQ7 consists of 192 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 21.7 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCOQ7 is approximately 20-25 kDa. |
| predicted N | Ser 37 |
| SDS-PAGE | 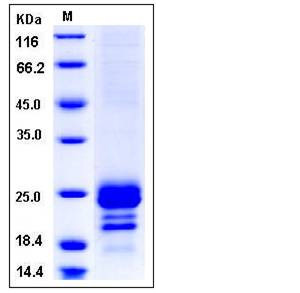 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the mature form of human COQ7 isoform 1 (Q99807-1) (Ser 37-Leu 217) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus and a signal peptide at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Types of disease |Metabolism in Cancer |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Ubiquinone biosynthesis protein COQ7 homolog, also known as Coenzyme Q biosynthesis protein 7 homolog, Timing protein clk-1 homolog and COQ7, is a mitochondrion inner membrane and peripheral membrane protein which belongs to the COQ7 family. It is expressed dominantly in heart and skeletal muscle. COQ7 is synthesized as a preprotein that is imported into the mitochondrial matrix, where the sequence is cleaved off and the mature protein becomes loosely associated with the inner membrane. This enzyme is responsible for the hydroxylation of 5-demethoxyubiquinone to 5-hydroxyubiquinone. Human COQ7 protein is mostly helical, and contains an alpha-helical membrane insertion. It has a potential N-glycosylation site, a phosphorylation site for protein kinase C and another for casein kinase II, and three N-myristoylation sites. COQ7 is involved in lifespan determination in ubiquinone-independent manner. It is also involved in ubiquinone biosynthesis. COQ7 is potential central metabolic regulator. |
| Reference |
