Human CROT Protein (474 Leu/Val, His Tag)
COT
- 100ug (NPP2054) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11015-H08B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | COT |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CROT consists of 623 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 71.5 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhCROT is approximately 65 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met 1 |
| SDS-PAGE | 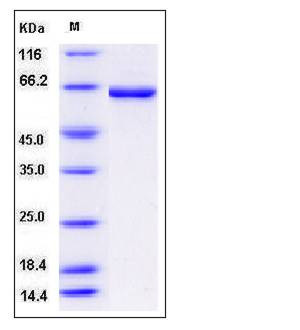 |
| Purity | > 93 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CROT (Q9UKG9) (Met 1-Leu 612, 474 Leu/Val) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cancer |Cancer Metabolism |Metabolic signaling |Metabolism of lipids and lipoprotein |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM Tris, 100mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% glycerol 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carnitine octanoyltransferase (CROT or COT), also known as octanoyl-CoA: L-carnitine O-octanoyltransferase, medium-chain/long-chain carnitine acyltransferase, and carnitine medium-chain acyltransferase, is a carnitine acyltransferase belonging to the family of transferases, specifically those acyltransferases transferring groups other than aminoacyl groups that catalyzes the reversible transfer of fatty acyl groups between CoA and carnitine. Carnitine octanoyltransferase (CROT or COT) facilitate the transport of medium- and long-chain fatty acids through the peroxisomal and mitochondrial membranes. It is physiologically inhibited by malonyl-CoA. COT also has functions in efficiently converting one of the end products of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation of pristanic acid, 4, 8-dimethylnonanoyl-CoA, to its corresponding carnitine ester. |
| Reference |
