Human CRTAM Protein (His Tag)
CD355
- 100ug (NPP3771) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11975-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CD355 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CRTAM consists of 280 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 31.4 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCRTAM is approximately 50-60 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 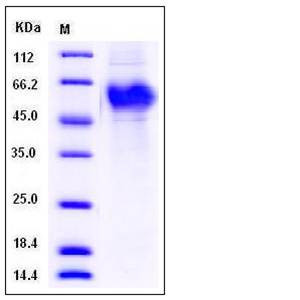 |
| Purity | > 94 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CRTAM (NP_062550.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ser 286) was expressed, with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA . Immobilized human CADM1 at 2 μg/ml (100 μl/well) can bind biotinylated human CRTAM with a linear range of 12.5-400 ng/ml. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Natural Killer Cell (NK Cell) |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cytotoxic and regulatory T-cell molecule, also known as Class-I MHC-restricted T-cell-associated molecule and CRTAM, is a single-pass type I membrane protein which belongs to the nectin family. CRTAM contains one Ig-like C2-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain and one Ig-like V-type (immunoglobulin-like) domain. In the immune system, the expression of CRTAM is restricted to activated class-I MHC-restricted cells, including NKT and CD8 cells. It is strongly expressed in spleen, thymus, small intestine, peripheral blood leukocyte, and in purkinje neurons in cerebellum. It is expressed at much lower levels in testis, ovary, colon, lung and lymphoid tissues. CRTAM is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily that complies with the structural characteristics of the JAM family of proteins and is phylogenetically more closely related to nectin-like proteins. It is a molecule involved in epithelial cell adhesion. CRTAM is sensitive to intermediate filament disruption and treatment of monolayers with soluble CRTAM enhances cell-cell dissociation and lowers transepithelial electrical resistance. CRTAM may also induce retention by binding to CD8+ dendritic cells (DCs) at the late stage of activation before proliferation. |
| Reference |
