Human CSK / C-Src kinase Protein (GST Tag)
MGC117393, CSK
- 100ug (NPP3617) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10740-H09B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | MGC117393, CSK |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CSK/GST chimera consists of 674 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 77 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 66 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 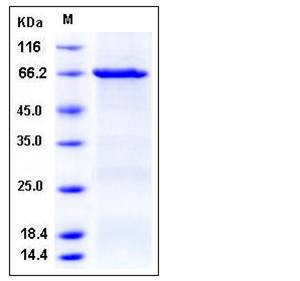 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CSK (NP_004374.1) (Met 1-Leu 450) was fused with the GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 127 nmol/min/mg using Poly(Glu,Tyr) 4:1 as substrate. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Protein Kinase |Intracellular Kinase |Src Family Kinase (SFK) |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, 0.5mM PMSF, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The tyrosine kinase c-Src has been implicated as a modulator of cell proliferation, spreading, and migration. These functions are also regulated by Met. The structure of a large fragment of the c-Src kinase comprises the regulatory and kinase domains and the carboxy-terminal tall. c-Src kinase interactions among domains and is stabilized by binding of the phosphorylated tail to the SH2 domain. This molecule is locked in a conformation that simultaneously disrupts the kinase active site and sequesters the binding surfaces of the SH2 and SH3 domains. The structure shows how appropriate cellular signals, or transforming mutations in v-Src, could break these interactions to produce an open, active kinase. The protein-tyrosine kinase activity of c-Src kinase is inhibited by phosphorylation of tyr527, within the c-Src c-terminal tail. Genetic and biochemical data have suggested that this negative regulation requires an intact Src homology 2 (SH2) domain. Since SH2 domains recognize phosphotyrosine, it is possible that these two non-catalytic domains associate, and thereby repress c-Src kinase activity. Experiments have suggested that c-Src kinase plays a role in the biological behaviour of colonic carcinoma cells induced by migratory factors such as EGF, perhaps acting in conjunction with FAK to regulate focal adhesion turnover and tumour cell motility. Furthermore, although c-Src kinase has been implicated in colonic tumour progression, in the adenoma to carcinoma in vitro model c-Src is not the driving force for this progression but co-operates with other molecules in carcinoma development. |
| Reference |
