Human CST9L / Testatin Protein (Fc Tag)
bA218C14.1,CTES7B,PRO3543,UNQ1835
- 100ug (NPP3782) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13243-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | bA218C14.1,CTES7B,PRO3543,UNQ1835 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CST9L/Fc chimera is a disulfide-linked homodimeric protein. The reduced monomer consists of 360 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 41.3 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCST9L/Fc monomer is approximately 48 kDa. |
| predicted N | Trp 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 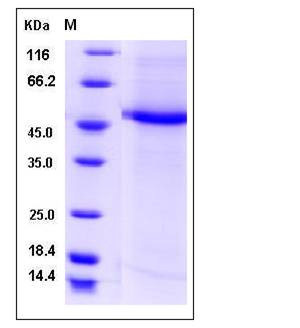 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CST9L (Q9H4G1) (Met 1-His 147) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Testatin is a member of the Cystatin family. Cystatins comprise genes that all show expression patterns that are strikingly restricted to reproductive tissue. Cystatins are a family of cysteine protease inhibitors with homology to chicken cystatin. There are typically about 115 amino acids in this family. They are largely acidic, contain four conserved cysteine residues known to form two disulfide bonds, may be glycosylated and/or phosphorylated, with similarity to fetuins, kininogens, stefins, histidine-rich glycoproteins and cystatin-related proteins. Testatin shows homology to family 2 cystatins, a group of broadly expressed small secretory proteins that are inhibitors of cysteine proteases in vitro but whose in vivo functions are unclear. It is expressed in germ cells and somatic cells in reproductive tissues. Testatin is considered a strong candidate for involvement in early testis development. Testatin expression is maintained in the adult Sertoli cell, and it can also be found in a small population of germ cells. |
| Reference |
