Human CTRL-1 / CTRL / Chymotrypsin-like protease Protein (His Tag)
CTRL1
- 100ug (NPP2059) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P13748-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CTRL1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CTRL consists of 257 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 27.6 KDa. It migrates as an approximately 35 and 32KDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Cys 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 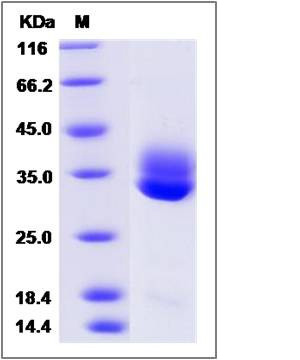 |
| Purity | (36.0+62.4) % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CTRL (P40313) (Met1-Asn264) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4. 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | CTRL-1, also known as chymotrypsin-like protease, belongs to the peptidase S1 family. CTRL-1 contains 1 peptidase S1 domain. Its expression is increased in preeclampsia (PE). Placental-derived chymotrypsin-like protease is responsible for inducing endothelial inflammatory phenotypic changes possibly by upregulation of cell adhesion molecule expressions, activation of cellular protease, and induction of extracellular regulated kinase phosphorylation. Activated microglia have been observed in various neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, and multiple sclerosis. Five structurally distinct inhibitors that are known to inhibit chymotrypsin-like proteases were partially protective. They might represent a novel class of drugs with benefit in diseases where overactivity of microglia contributes to the pathogenesis. |
| Reference |
