Human CTSZ Protein (His Tag)
CTSX
- 100ug (NPP3785) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10159-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CTSX |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CTSZ (pro form) consists of 291 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 33 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhCTSZ is approximately 40 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gly 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 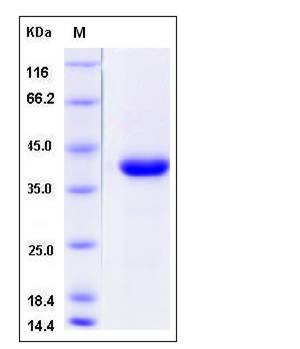 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CTSZ (Q9UBR2) (Met 1-Val 303) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Mca-RPPGFSAFK (Dnp)-OH,R&D Systems, Catalog # ES005. The specific activity is >800 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsin Z (CTSZ), also known as Cathepsin X or CATX, belongs to the C1 family of lysosomal cysteine proteases. Its gene structure and activity properties show several unique features that distinguish it clearly from other human cysteine proteases. It has a very short pro-region that shows no similarity to those of other cathepsins and a three-residue insertion motif that forms a characteristic ‘mini loop’. Cathepsin Z exhibits mono- and di-peptidase activity at its C-terminus, and in contrast to cathepsin B, it does not act as an endopeptidase. It is restricted to the cells of theimmune system, predominantly monocytes, macrophages and dendritic cells. Cathepsin Z is widely expressed in human tissues, suggesting that this enzyme could be involved in the normal intracellular protein degradation taking place in all cell types. It is capable to cleave regulatory motifs at C-terminus affecting the function of targeted molecules. Cathepsin X may regulate also the maturation of dendritic cells, a process, which is crucial in the initiation of adaptive immunity. Furthermore, higher levels of Cathepsin Z are also found in tumour and immune cells of prostate and gastric carcinomas and inmacrophages of gastric mucosa, especially after infection by Helicobacter pylori. Cathepsin Z is also ubiquitously distributed in cancer cell lines and in primary tumors from different sources, suggesting that this enzyme may participate in tumor progression. |
| Reference |
