Human Cadherin-12 / CDH12 Protein (His Tag)
CDHB
- 100ug (NPP3622) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10317-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CDHB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDH12 comprises 593 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 66 kDa. The apparent molecular mass of rhCDH12 is approximately 80-85 kDa in SDS-PAGE due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 24 |
| SDS-PAGE | 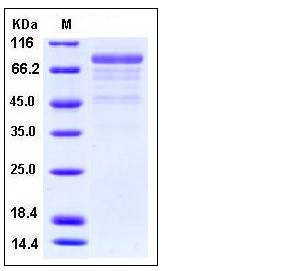 |
| Purity | > 80 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pro form of human CDH12 (NP_001783.2) extracellular domain (Met 1-Ala 605) was fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 50mM sodium citrate, 50mM NaCl, 2mM CaCl2, pH 6.0 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Classic Cadherins represent a family of calcium-dependent homophilic cell-cell adhesion molecules. They confer strong adhesiveness to animal cells when they are anchored to the actin cytoskeleton via their cytoplasmic binding partners, catenins. The cadherin/catenin adhesion system plays key roles in the morphogenesis and function of the vertebrate and invertebrate nervous systems. Furthermore, this system is involved in synaptic plasticity. Recent studies on the role of individual cadherin subtypes at synapses indicate that individual cadherin subtypes play their own unique role to regulate synaptic activities. Type II (atypical) cadherins are defined based on their lack of an HAV cell adhesion recognition sequence specific to type I cadherins. It has been observed that cells containing a specific cadherin subtype tend to cluster together to the exclusion of other types, both in cell culture and during development. Cadherin-12 also known as CDH12, is a type II classical cadherin from the cadherin superfamily of integral membrane proteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion. Cadherin-12 appears to be expressed specifically in the brain and its temporal pattern of expression would be consistent with a role during a critical period of neuronal development, perhaps specifically during synaptogenesis. |
| Reference |
