Human Cadherin-17 / LI-cadherin / CDH17 Protein (His Tag)
CDH16,HPT-1,HPT1
- 100ug (NPP3623) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11360-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CDH16,HPT-1,HPT1 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CDH17 consists of 776 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 87 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh CDH17 is approximately 105-115 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 23 |
| SDS-PAGE | 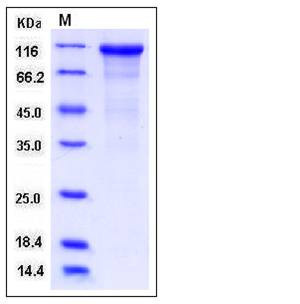 |
| Purity | > 88 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CDH17 (Q12864-1) extracellular domain (Met 1-Met 787) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by the ability of the immobilized protein to support the adhesion of MCF-7 human breast adenocarcinoma cells. When 5 x 10E4 cells/well are added to Recombinant Human Cadherin-17 coated plates (5 μg/mL with 100 μL/well), approximately > 30% will adhere after 1 hour at 37℃. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cadherin-17 or LI-cadherin is a member of the cadherin superfamily, genes encoding calcium-dependent, membrane-associated glycoproteins. Cadherin-17/LI-cadherin is a cadherin-like protein consisting of an extracellular region, 7 cadherin domains, and a transmembrane region but lacking the conserved cytoplasmic domain. The protein is a component of the gastrointestinal tract and pancreatic ducts, acting as an intestinal proton-dependent peptide transporter in the first step in oral absorption of many medically important peptide-based drugs. The protein may also play a role in the morphological organization of liver and intestine. Alternative splicing of the encoding gene results in multiple transcript variants. Cadherin-17/LI-cadherin preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells. Cadherin-17 may thus contribute to the sorting of heterogeneous cell types and have a role in the morphological organization of liver and intestine. It's also involved in intestinal peptide transport. Experiments have reported the association between Cadherin-17/LI-cadherin and gastric cancer. Cadherin-17/LI-cadherin expression was detected in 63/94 of gastric adenocarcinomas in addition to intestinal metaplasia. The expression of Cadherin-17 tended to be associated with intestinal type carcinoma, and carcinomas with Cadherin-17 expression was significantly more frequent in advanced stage cases than in early stage. Cadherin-17 is also a useful immunohistochemical marker for diagnosis of adenocarcinomas of the digestive system. |
| Reference |
