Human Cadherin-8 / CDH8 Protein (His Tag)
Nbla04261
- 100ug (NPP3625) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10144-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | Nbla04261 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted pro form of human CDH8 consists of 603 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 66.6 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, it migrates with an apparent molecular mass of 85-90 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 30 |
| SDS-PAGE | 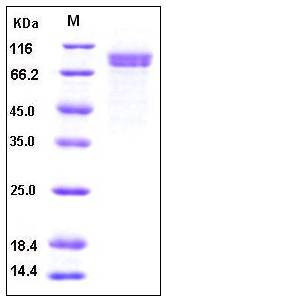 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the extracellular domain of human CDH8 (NP_001787.2) (Met 1-Met 621) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Cytoskeleton / ECM |Cell Adhesion |Cadherins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cadherins are integral membrane proteins that mediate calcium-dependent cell-cell adhesion. Type I cadherin proteins are composed of a large N-terminal extracellular domain, a single membrane-spanning domain, and a small, highly conserved C-terminal cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain consists of five subdomains, each containing a cadherin motif, and appears to determine the specificity of the protein's homophilic cell adhesion activity. Type II (atypical) cadherins are defined based on their lack of a HAV cell adhesion recognition sequence specific to type I cadherins. Cadherin 8, also known as CDH 8, is a type I I classical cadherin belonging to the cadherin superfamily. As mainly expressed in brain, CDH8 is found in certain nerve cell lines, such as retinoblasts, glioma cells and neuroblasts, and is putatively involved in synaptic adhesion, axon outgrowth and guidance. Human Cadherin 8 is a 799 amino acid single-pass type I transmembrane protein with a putative 29 aa signal sequence, and a 32 aa propeptide, a 560 aa mature extracellular domain, a 21 aa transmembrane domain and a 157 aa cytoplasmic domain. The human, mouse and rat proteins share approximately 98% homology. |
| Reference |
