Human Carbonic Anhydrase IV / CA4 Protein (His Tag)
CAIV,Car4,RP17
- 100ug (NPP1960) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10472-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CAIV,Car4,RP17 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CA4 consists of 276 amino acids after removal of the signal peptide and has a predicted molecular mass of 31.7 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, rh CA4 migrates as an approximately 30 kDa band. |
| predicted N | Ala 19 |
| SDS-PAGE | 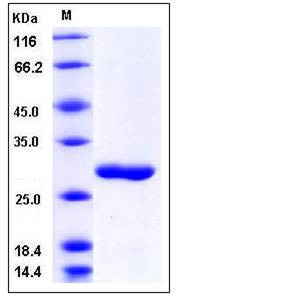 |
| Purity | > 96 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CA4 (NP_000708.1) (Met1-Lys283) without the pro peptide was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its esterase activity . The specific activity is >2 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Cancer |Signal transduction |Metabolism |Mitochondrial |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | The carbonic anhydrases (or carbonate dehydratases) are classified as metalloenzyme for its zinc ion prosthetic group and form a family of enzymes that catalyze the rapid interconversion of carbon dioxide and water to bicarbonate and protons, a reversible reaction that takes part in maintaining acid-base balance in blood and other tissues. The carbonic anhydrasekl (CA) family consists of at least 11 enzymatically active members and a few inactive homologous proteins. Carbonic anhydrase IV (CAIV) is a membrane-associated enzyme anchored to plasma membrane surfaces by a phosphatidylinositol glycan linkage. CAIV is a high-activity isozyme in CO2 hydration comparable to that of CAII. Furthermore, CAIV is more active in HCO3- dehydration than is CAII. However, the esterase activity of CAIV is decreased 150-fold compared to CAII. |
| Reference |
