Human Carbonic Anhydrase IX / CA9 Protein (Fc Tag)
CAIX,Carbonic Anhydrase IX,MN
- 100ug (NPP1961) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10107-H02H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CAIX,Carbonic Anhydrase IX,MN |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CA9/Fc is a disulfide-linked homodimer. The reduced monomer consists of 615 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 67.7 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, the apparent molecular mass of rh CA9/Fc monomer is approximately 80-90 kDa in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 38 |
| SDS-PAGE | 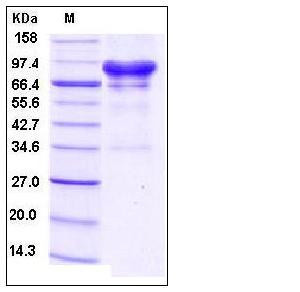 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human carbonic anhydrase IX (CA9) precursor (NP_001207.2) (Met 1-Asp 414) was fused with the Fc region of human IgG1 at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its esterase activity. The specific activity is >50 pmoles/min/μg, as measured with 1 mM 4-Nitrophenyl acetate and 1 μg enzyme at 400 nm in 100 μL of 12.5 mM Tris, 75 mM NaCl, pH 7.5. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Signaling Pathway |Calcium Signaling |Calcium Binding Proteins |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 100mM Glycine, 10mM NaCl, 50mM Tris, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carbonic anhydrases IX (CA IX), also known as membrane antigen MN or CA9, is a member of the carbonic anhydrase (CA) family and may be involved in cell proliferation and cellular transformation. CAs are zinc metalloenzymes that catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide (H2O + CO2 = H+ + HCO3–) and thus participate in a variety of biological and physical processes. CA IX protein is expressed primarily in carcinoma cells lines, and the expression is cell density dependent and has been shown to be strongly induced by hypoxia, accordingly facilitates adaptation of tumor cells to hypoxic conditions. It is involved in tumorigenesis through many pathways, such as pH regulation and cell adhesion control. CA IX is used as a marker of tumor hypoxia and as a new therapeutic target for many human carcinomas and cancers. |
| Reference |
