Human Carbonic Anhydrase X / CA10 Protein (His Tag)
CA-RPX,CA10,CARPX,HUCEP-15
- 100ug (NPP1965) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10687-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CA-RPX,CA10,CARPX,HUCEP-15 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CARPX consists of 291 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 33 kDa. rhCARPX migrates as an approximately 37 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Gln 22 |
| SDS-PAGE | 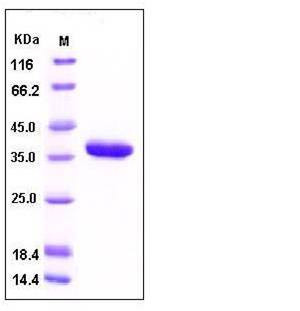 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CARPX (NP_001076002.1) (Met 1-Asn 300) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its esterase activity. The specific activity is >10 pmoles/min/μg, as measured with 1 mM 4-Nitrophenyl acetate and 5 μg enzyme at 400 nm in 100 μL of 12.5 mM Tris, 75 mM NaCl, pH 7.5. |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Cardiovascular disease Therapeutic Targets |Hypertension Therapeutic Targets |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Carbonic anhydrase X, also called carbonic anhydrase - related protein X (CARPX) and CA10, belongs to the CA family of zinc metalloenzymes which catalyze the reversible hydration of carbon dioxide in various biological processes such as respiration, renal tubular acidification and bone resorption. The secreted protein CARPX without CA activity (hydration of CO2) is identified as an acatalytic member of the alpha-carbonic anhydrase subgroup. CARP X expression is detected in the adult total brain and almost all parts of the central nervous system, but not in the fetal brain. Accordingly, CARP X is suggested to play a role in the development of central nervous system, especially the brain. The same CARP X protein are encoded by multiple transcript variants of this gene. |
| Reference |
