Human Carboxypeptidase A1 / CPA1 Protein (His Tag)
CPA
- 100ug (NPP1968) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10504-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CPA |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CPA1 (pro form) consists of 414 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 47 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, it migrates with the apparent molecular mass of 43 kDa. |
| predicted N | Lys 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 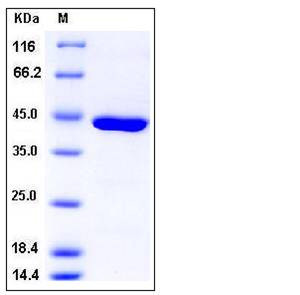 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human CPA1 precursor (NP_001859.1) (Met 1-Tyr 419) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the colorimetric peptide substrate Ac-Phe-Thiaphe-OH in the presence of 5,5'Dithiobis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB). The specific activity is >3,500 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Microbiology |Pathogenic microorganism |viruses |animal virus |viral illness |Skin or mucous membranes illness | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human Carboxypeptidase A1 (CPA1)is secreted as a pancreatic procarboxypeptidase, and cleaves the C-terminal amide or ester bond of peptides that have a free C-terminal carboxyl group, with the preference of residues with aromatic or branched aliphatic side chains. CPA1 comprises a signal peptide, a pro region and a mature chain, and can be activated after cleavage of the pro peptide. In contrast to procarboxypeptidase B which was always secreted by the pancreas as a monomer, procarboxypeptidase A occurs as a monomer and/or associated to one or two functionally different proteins, such as zymogen E, and is involved in zymogen inhibition. Three different forms of human pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A have been isolated. |
| Reference |
