Human Carboxypeptidase A2 / CPA2 Protein (His Tag)
CPA2
- 100ug (NPP1969) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10499-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CPA2 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CPA2 existing as the proform consists of 412 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 46 kDa also as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Leu 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 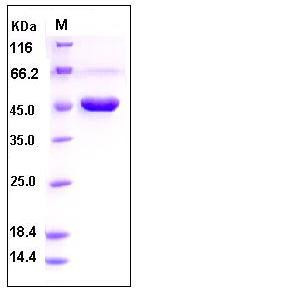 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pre pro form of human CPA2 (NP_001859.1) (Met 1-Tyr 417) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave a colorimetric peptide substrate, N-acetyl-Phe-Thiaphe-OH (N-Ac-PSP, Peptide International's Catalog# STP-3621-PI), in the presence of 5,5'Dithio-bis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) (DTNB), as measured using the wavelength at 405 nm and the extinction coefficient of 13,260 M-1 cm-1. The specific activity is >4,000 pmoles/min/μg . |
| Research Area | Cancer |Oncoprotein & suppressor & biomarker |Tumor biomarker |Other in cancer biomarker |Globulin |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 0.15mM NaCl, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Human Carboxypeptidase A2 ( CPA2 ) is a secreted pancreatic procarboxy -peptidase, and cleaves the C-terminal amide or ester bond of peptides that have a free C-terminal carboxyl group. The hydrolytic action of CPA2 was identified with a preference towards long substrates with aromatic amino acids in their C-terminal end, particularly tryptophan. CPA2 comprises a signal peptide, a pro region and a mature chain, and can be activated after cleavage of the pro peptide. Three different forms of human pancreatic procarboxypeptidase A have been isolated, and the A1 and A2 forms are always secreted as monomeric proteins with different biochemical properties. |
| Reference |
