Human Cathepsin A / CTSA Protein (His Tag)
GLB2,GSL,NGBE,PPCA,PPGB
- 100ug (NPP3643) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10482-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | GLB2,GSL,NGBE,PPCA,PPGB |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CTSA existing as a single-chain form consists of 463 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 53 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Ala 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 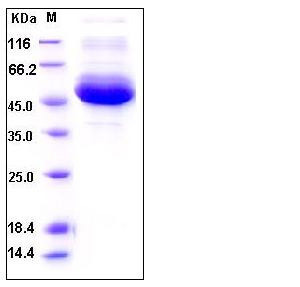 |
| Purity | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human cathepsin A isoform b (Met 1-Tyr 480) (NP_001121167.1) was expressed with a N-terminal signal peptide and a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Immunology |Signal Transduction |Metabolism |Pathways and Processes |Metabolic signaling pathways |Amino acid metabolism | |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM Tris, 0.15mM NaCl, pH 7.5 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Lysosomal carboxypeptidase, cathepsin A (protective protein, CathA), is a component of the lysosomal multienzyme complex along with beta-galactosidase (GAL) and sialidase Neu1, where it activates Neu1 and protects GAL and Neu1 against the rapid proteolytic degradation. Cathepsin A is a multicatalytic enzyme with deamidase and esterase in addition to carboxypeptidase activities. It was recently identified in human platelets as deamidase. In vitro, it hydrolyzes a variety of bioactive peptide hormones including tachykinins, suggesting that extralysosomal cathepsin A plays a role in regulation of bioactive peptide functions. It is a member of the alpha/beta hydrolase fold family and has been suggested to share a common ancestral relationship with other alpha/beta hydrolase fold enzymes, such as cholinesterases. Cathepsin A defects are linked to multiple forms of Galactosialidosis with a combined secondary deficiency of beta-galactosidase and neuraminidase. Cathepsin A is a key molecule in the onset of galactosialidosis and also highlight the therapeutic acts in vivo as an endothelin-1-inactivating enzyme and strongly confirm a crucial role of this enzyme in effective elastic fiber formation. |
| Reference |
