Human Cathepsin B / CTSB Protein (His Tag)
APPS,CPSB
- 100ug (NPP3644) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10483-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | APPS,CPSB |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human CTSB existing as the proform consists of 332 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 37.2 kDa. rhCTSB migrates with the molecular weight of 36 and 43 kDa as the proform and mature form rspectively in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Arg 18 & Phe 74 |
| SDS-PAGE | 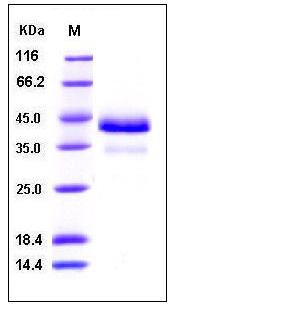 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pre pro form of human CTSB (Arg18-Ile339) (NP_001899.1) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-LR-AMC (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES008) . The specific activity is >2,500 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Inflammation / Inflammatory Mediator |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsin B is a papain-family cysteine protease that is normally located in lysosomes, where it is involved in the turnover of proteins and plays various roles in maintaining the normal metabolism of cells. This protease has been implicated in pathological conditions, e.g., tumor progression and arthritis. In disease conditions, increases in the expression of cathepsin B occur at both the gene and protein levels. Cathepsin B is synthesized as a preproenzyme and the primary pathways for its normal trafficking to the lysosome utilize mannose 6-phosphate receptors (MPRs). Mature cathepsin B has the ability to degrade several extracellular matrix components at both neutral and acidic pH and has been implicated in the progression of several human and rodent tumors progression and arthritis. Cathepsin B expression is increased in many human cancers at the mRNA, protein and activity levels. It is also frequently overexpressed in premalignant lesions, an observation that associates this protease with local invasive stages of cancer. Increased expression of cathepsin B in primary cancers, and especially in preneoplastic lesions, suggests that this enzyme might have pro-apoptotic features. Active cathepsin B is also secreted from tumours, a mechanism likely to be facilitated by lysosomal exocytosis or extracellular processing by surface activators. Cathepsin B is localized to caveolae on the tumour surface, where binding to the annexin II heterotetramer occurs. Thus CTSB is suggested as a tumor marker. Additionally, Cathepsin B can degrade extracellular matrix proteins, such as collagen IV and laminin, and can activate the precursor form of urokinase plasminogen activator (uPA), perhaps thereby initiating an extracellular proteolytic cascade. |
| Reference |
|
