Human Cathepsin C / CTSC / DPPI Protein (His Tag)
CPPI,DPP-I,DPP1,DPPI,HMS,JP,JPD,PALS,PDON1,PLS
- 100ug (NPP3645) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10484-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CPPI,DPP-I,DPP1,DPPI,HMS,JP,JPD,PALS,PDON1,PLS |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human cathepsin C exists as the pro form after removal of the signal peptide. It consists of 450 amino acids and has a predicted molecular mass of 51 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rhCTSC is approximately 55 kDa. |
| predicted N | Asp 25 |
| SDS-PAGE | 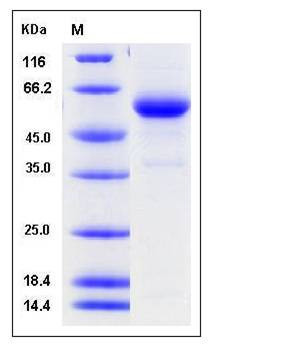 |
| Purity | > 92 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pro form of human cathepsin C (NP_001805.3) (Met 1-Leu 463) was expressed with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate, Gly-Arg-7-amido-4-methylcoumarin (GRAMC). The specific activity is >200 pmoles/min/μg. (Activation description: The proenzyme needs to be activated by Cathepsin L for an activated form) |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsins are proteases found in many types of cells conserved in all animals, which have a vital role in mammalian cellular turnover such as bone resorption. The lysosomal cysteine protease Cathepsin C (CTSC), also known as dipeptidyl peptidase I (DPPI/DPP1), activates a number of granule-associated serine proteases with pro-inflammatory and immune functions by removal of their inhibitory N-terminal dipeptides. This lysosomal exo-cysteine protease belonging to the peptidase C1 family. Active cathepsin C is found in lysosomes as a 200-kDa multimeric enzyme. Subunits constituting this assembly all arise from the proteolytic cleavage of a single precursor giving rise to three peptides: the propeptide, the alpha- and the beta-chains. It is a central coordinator for activation of many serine proteases in immune/inflammatory cells. Defects in the Cathepsin C have been shown to be a cause of Papillon-Lefevre disease, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by palmoplantar keratosis and periodontitis. Cathepsin C plays a key role in the activation of several degradative enzymes linked to tissue destruction in inflammatory diseases. Thus, it is a therapeutic target for the treatment of a number of inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. |
| Reference |
