Human Cathepsin S / CTSS Protein (His Tag)
CTSS,MGC3886
- 100ug (NPP3648) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10487-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CTSS,MGC3886 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human CTSS consists of 326 amino acids with the predicted molecular mass of 37 kDa as estimated by SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Gln 17 |
| SDS-PAGE | 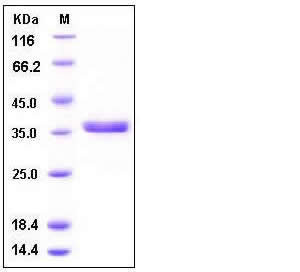 |
| Purity | > 97 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the pro form of human CTSS (NP_004070.3) (Met 1-Ile 331) with a carboxy-terminal polyhistidine tag was expressed. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave a fluorogenic peptide substrate, (7-methoxycoumarin-4-yl) acetyl-Arg-Pro-Lys-Pro-Val-Glu-Nva-Trp-Arg-Lys (2, 4-dinitrophenyl)-NH2 (R&D Systems, Catalog#ES002). Cleavage of ES002 can be measured using excitation and emission wavelength at 320 nm and 405 nm, respectively. The specific activity is >300 pmoles/min/μg . (Activation description: The enzyme achieves its activity under acidic pH) |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Organogenesis |Skeletal development |Other Bone Remodeling Molecules |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsin S (CTSS), one of the lysosomal proteinases, has many important physiological functions in the nervous system, especially in process of extracellular matrix degradation and endocellular antigen presentation. CTSS is synthesized as inactive precursor of 331 amino acids consisting of a 15-aa signal peptide, a propeptide of 99 aa, and a mature polypeptide of 217 aa. It is activated in the lysosomes by a proteolytic cleavage of the propeptide. Cathepsin S is expressed in the lysosome of antigen presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells, B-cells and macrophages. Compared with other lysosomal cysteine proteases, cathepsin S has displayed some unique characteristics. Cathepsin S is most well known for its critical function in the proteolytic digestion of the invariant chain chaperone molecules, thus controlling antigen presentation to CD4+ T-cells by major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules or to NK1.1+ T-cells via CD1 molecules. Cathepsin S also appears to participate in direct processing of exogenous antigens for presentation by MHC class II to CD4+ T-cells, or in cross-presentation by MHC class I molecules to CD8+ T-cells. In addition, although direct evidence is still lacking, in its secreted form cathepsin S is implicated in degradation of the extracellular matrix, which may contribute to the pathology of a number of diseases, including arthritis, atherosclerosis, neurological diseases and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. |
| Reference |
