Human Cathepsin V / Cathepsin L2 / Preproprotein Protein (His Tag)
CATL2,CTSL2,CTSU,CTSV,MGC125957
- 100ug (NPP3649) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10093-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | CATL2,CTSL2,CTSU,CTSV,MGC125957 |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant pro form of human cathepsin V comprises 328 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 37.1 kDa. As a result of glycosylation, it migrates as an approximately 40 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Val 18 |
| SDS-PAGE | 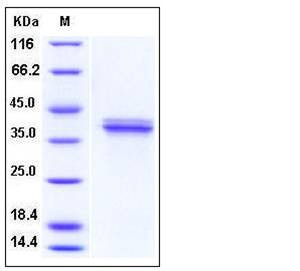 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the full length of human cathepsin L2 (NP_001324.2) (Met 1-Val 334) was expressed, with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to cleave the fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-LR-AMC, (R&D Systems, Catalog # ES008) . The specific activity is >1000 pmoles/min/μg. |
| Research Area | Immunology |Innate Immunity |Lysosomal Enzymes |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cathepsin V (CTSV), also known as Cathepsin L2, CTSL2, and CATL2, is a member of the peptidase C1 family. It is predominantly expressed in the thymus and testis. Cathepsin V is also expressed in corneal epithelium, and to a lesser extent in conjuctival epithelium and skin. It is a lysosomal cysteine proteinase that may play an important role in corneal physiology. It has about 75% protein sequence identity to murine cathepsin L. The fold of this enzyme is similar to the fold adopted by other members of the papain superfamily of cysteine proteases. Cathepsin V has been recently described as highly homologous to Cathepsin L and exclusively expressed in human thymus and testis. Cathepsin V is the dominant cysteine protease in cortical human thymic epithelial cells, while Cathepsin L and Cathepsin S seem to be restricted to dendritic and macrophage-like cells. Active Cathepsin V in thymic lysosomal preparations was demonstrated by active-site labeling. Recombinant Cathepsin V was capable of converting Ii into CLIP efficiently, suggesting that it is the protease that controls the generation of alphabeta-CLIP complexes in the human thymus. Cathepsin V is the third elastolytic cysteine protease which exhibits the most potent elastase activity yet described among human proteases and that it is present in atherosclerotic plaque specimens. Cathepsin L2 may play a specialized role in the thymus and testis. Expression analysis of cathepsin L2 in human tumors revealed a widespread expression in colorectal and breast carcinomas but not in normal colon or mammary gland or in peritumoral tissues. Cathepsin L2 was also expressed by colorectal and breast cancer cell lines as well as by some tumors of diverse origin, including ovarian and renal carcinomas. |
| Reference |
