Human Coagulation Factor IX / FIX / F9 Protein (His Tag)
FIX,HEMB,P19,PTC,THPH8
- 100ug (NPP1204) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11503-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | FIX,HEMB,P19,PTC,THPH8 |
| Molecular Weight | The secreted recombinant human F9 (pro form) consists of 444 amino acids and predictes a molecular mass of 50 kDa. In SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions, the apparent molecular mass of rh F9 is approximately 60-80 kDa due to glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Thr 29 |
| SDS-PAGE | 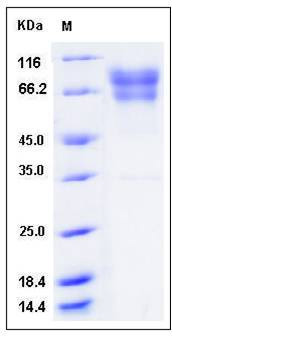 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human F9 (AAB59620.1) (Met 1-Thr 461) was expressed, fused with a polyhistidine tag at the C-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | |
| Research Area | Cardiovascular |Blood |Other in Blood |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 7.4 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Coagulation factor IX, also known as Christmas factor, Plasma thromboplastin component and PTC, is a secreted protein which belongs to the peptidase S1 family. Coagulation factor IX / F9 contains two EGF-like domains, one Gla (gamma-carboxy-glutamate) domain and one?peptidase S1 domain. Coagulation factor IX / F9 is a vitamin K-dependent plasma protein that participates in the intrinsic pathway of blood coagulation by converting factor X to its active form in the presence of Ca2+ons, phospholipids, and factor VIIIa. Defects in Coagulation factor IX / F9 are the cause of thrombophilia due to factor IX defect which is a hemostatic disorder characterized by a tendency to thrombosis. Defects in Coagulation factor IX / F9 are also the cause of recessive X-linked hemophilia B ( HEMB ) which also known as Christmas disease. |
| Reference |
