Human Cystatin C / CST3 Protein (His Tag)
ARMD11
- 100ug (NPP3789) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P10439-H08H |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Human Cells |
| Synonyms | ARMD11 |
| Molecular Weight | The mature recombinant human Cystatin-C consists of 131 amino acids and predicts a molecular mass of 14.8 kDa. The rh Cystatin-C migrates as approximately 17 kDa band in SDS-PAGE as a result of glycosylation. |
| predicted N | Ser 27 |
| SDS-PAGE | 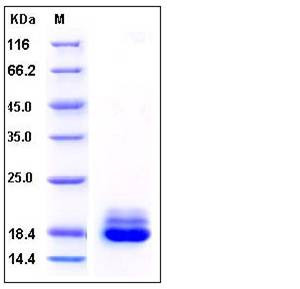 |
| Purity | > 95 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the human Cystatin-C (NP_000090.1) (Ser 27-Ala 146) was expressed with a C-terminal polyhistidine tag. |
| Bio-activity | Measured by its ability to inhibit papain cleavage of a fluorogenic peptide substrate Z-FR-AMC,R&D Systems, Catalog # ES009. The IC50 value is < 12 nM . |
| Research Area | Developmental Biology |Metabolism |Vitamins / Minerals |
| Formulation | Lyophilized from sterile 25mM HEPES, 0.15mM NaCl, pH 7.7 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Cystatin C, also known as Cystatin-3 (CST3) is a secreted type 2 cysteine protease inhibitor synthesized in all nucleated cells, has been proposed as a replacement for serum creatinine for the assessment of renal function, particularly to detect small reductions in glomerular filtration rate. The mature, active form of human cystatin C is a single non-glycosylated polypeptide chain consisting of 120 amino acid residues, with a molecular mass of 13,343-13,359 Da, and containing four characteristic disulfide-paired cysteine residues. Cystatin C is a low-molecular-weight protein which has been proposed as a marker of renal function that could replace creatinine. Indeed, the concentration of Cystatin C is mainly determined by glomerular filtration and is particularly of interest in clinical settings where the relationship between creatinine production and muscle mass impairs the clinical performance of creatinine. Since the last decade, numerous studies have evaluated its potential use in measuring renal function in various populations. More recently, other potential developments for its clinical use have emerged. In almost all the clinical studies, Cystatin C demonstrated a better diagnostic accuracy than serum creatinine in discriminating normal from impaired kidney function, but controversial results have been obtained by comparing this protein with other indices of kidney disease, especially serum creatinine-based equations, such as early atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's dementia, vascular aneurysms, hyperhomocysteinaemia and other neurodegenerative diseases. Cystatin C could be a useful clinical tool to identify HIV-infected persons. In addition, its expression is up-regulated in malignance of certain tumor progression. |
| Reference |
