Human DAPK1 / DAP Kinase 1 Protein (aa 1-363, His & GST Tag)
DAPK
- 100ug (NPP3792) Please inquiry
| Catalog Number | P11966-H20B |
|---|---|
| Organism Species | Human |
| Host | Baculovirus-Insect Cells |
| Synonyms | DAPK |
| Molecular Weight | The recombinant human DAPK1 (aa 1-363)/GST chimera consists of 600 amino acids and has a calculated molecular mass of 69.4 kDa. It migrates as an approximately 64 kDa band in SDS-PAGE under reducing conditions. |
| predicted N | Met |
| SDS-PAGE | 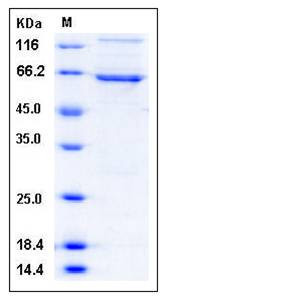 |
| Purity | > 85 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Protein Construction | A DNA sequence encoding the N-terminal segment of human DAPK1 (P53355-1) (Met 1-Leu 363) was fused with the N-terminal polyhistidine-tagged GST tag at the N-terminus. |
| Bio-activity | The specific activity was determined to be 20 nmol/min/mg using synthetic R11-S6-Peptide (R11-IAKRRRLSSLRASTSKSESSQK) as substrate. |
| Research Area | Signaling |Signal Transduction |Cellular Senescence and Pathways in Aging |Apoptosis |Extracellular Signals |Death Ligands | |
| Formulation | Supplied as sterile 20mM Tris, 500mM NaCl, pH 8.0, 10% gly 1. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose and mannitol are added as protectants before lyophilization. Specific concentrations are included in the hardcopy of COA. |
| Background | Death-associated protein kinase 1, also known as DAP kinase 1, DAPK1 and DAPK, is a cytoplasm protein which belongs to the protein kinase superfamily, CAMK Ser / Thr protein kinase family and DAP kinase subfamily. DAPK1 contains ten ANK repeats, one death domain and one protein kinase domain. DAPK1 is a calcium / calmodulin-dependent serine/threonine kinase which acts as a positive regulator of apoptosis. DAPK1 gene is a candidate tumor suppressor (TSG) and the abnormal methylation of DAPK1 gene has been found in many carcinomas. DAPK1 over-expression can induce cell apoptosis and inhibit tumor cell metastasis. DAPK1 gene over-expression could suppress PGCl3 cells malignant phenotype, inhibit PGCl3 cells growth, invasive, migration and adhesion ability, upregulate p53 gene and downregulate bcl-2 gene. Loss of activity of death-associated protein kinase 1 ( DAPK1 ) may be an independent factor affecting survival of non-small cell lung cancer patients. DAPK1 promoter methylation might play a significant role in the progression of chronic myeloid leukemia ( CML ). |
| Reference |
